A bimodal distribution is a probability distribution with two modes. We often use the term “mode” in descriptive statistics to refer to the most commonly occurring value in a dataset, but in this case the term “mode” refers to a local maximum in a chart. When you visualize a bimodal distribution, you will notice two distinct “peaks
256 Shades of Gray: Improve Your Photography Using Your Camera’s Histogram | Fstoppers
Graph 2.2.1: Histogram for Monthly Rent. Notice the graph has the axes labeled, the tick marks are labeled on each axis, and there is a title. It is important that your graphs (all graphs) are clearly labeled. Reviewing the graph you can see that most of the students pay around $750 per month for rent, with about $1500 being the other common value.

Source Image: theintactone.com
Download Image
Jan 4, 2024Definition: Histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data. It consists of a series of bars, where the height of each bar represents the frequency or relative frequency of the data within a particular interval or “bin.”

Source Image: stackoverflow.com
Download Image
Chapter 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Fun Bimodal Distribution: Definition, Examples & Analysis By Jim Frost 1 Comment A bimodal distribution has two peaks. In the context of a continuous probability distribution, modes are peaks in the distribution. The graph below shows a bimodal distribution.

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
A Histogram Is If It Has Two Clearly Distinct Modes
Fun Bimodal Distribution: Definition, Examples & Analysis By Jim Frost 1 Comment A bimodal distribution has two peaks. In the context of a continuous probability distribution, modes are peaks in the distribution. The graph below shows a bimodal distribution. The mean, the median, and the mode are each seven for these data. In a perfectly symmetrical distribution, the mean and the median are the same. This example has one mode (unimodal), and the mode is the same as the mean and median. In a symmetrical distribution that has two modes (bimodal), the two modes would be different from the mean and median.
Chapter 2 Flashcards | Quizlet
A histogram is a chart that plots the distribution of a numeric variable’s values as a series of bars. Each bar typically covers a range of numeric values called a bin or class; a bar’s height indicates the frequency of data points with a value within the corresponding bin. Similarity of histograms for two images of a person (a) Match image 1,… | Download Scientific Diagram
Source Image: researchgate.net
Download Image
Water | Free Full-Text | Application of an Interval Two-Stage Robust (ITSR) Optimization Model for Optimization of Water Resource Distribution in the Yinma River Basin, Jilin Province, China A histogram is a chart that plots the distribution of a numeric variable’s values as a series of bars. Each bar typically covers a range of numeric values called a bin or class; a bar’s height indicates the frequency of data points with a value within the corresponding bin.
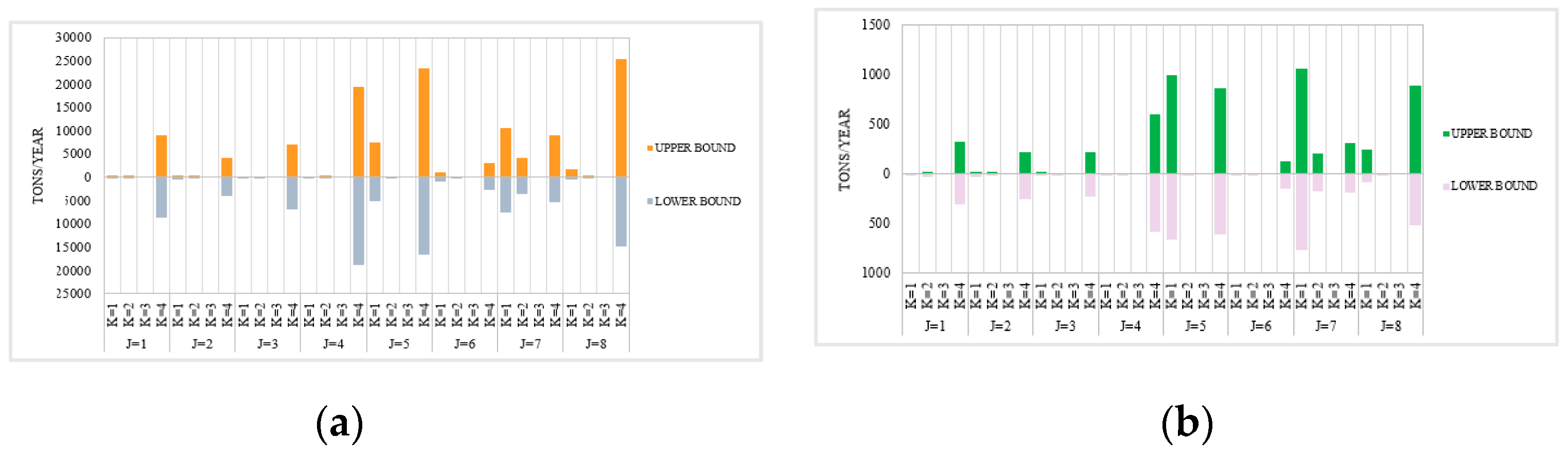
Source Image: mdpi.com
Download Image
256 Shades of Gray: Improve Your Photography Using Your Camera’s Histogram | Fstoppers A bimodal distribution is a probability distribution with two modes. We often use the term “mode” in descriptive statistics to refer to the most commonly occurring value in a dataset, but in this case the term “mode” refers to a local maximum in a chart. When you visualize a bimodal distribution, you will notice two distinct “peaks

Source Image: fstoppers.com
Download Image
Chapter 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Jan 4, 2024Definition: Histogram is a graphical representation of the distribution of numerical data. It consists of a series of bars, where the height of each bar represents the frequency or relative frequency of the data within a particular interval or “bin.”

Source Image: quizlet.com
Download Image
r – How to easily maintain the same axis scale for two histograms – Stack Overflow By Jim Frost 23 Comments. Histograms are graphs that display the distribution of your continuous data. They are fantastic exploratory tools because they reveal properties about your sample data in ways that summary statistics cannot. For instance, while the mean and standard deviation can numerically summarize your data, histograms bring your

Source Image: stackoverflow.com
Download Image
Solved Look at the two histograms below. Each involves the | Chegg.com Fun Bimodal Distribution: Definition, Examples & Analysis By Jim Frost 1 Comment A bimodal distribution has two peaks. In the context of a continuous probability distribution, modes are peaks in the distribution. The graph below shows a bimodal distribution.

Source Image: chegg.com
Download Image
Communication Design — Project 4 — Kyle Lee | by Kyle Lee | Medium The mean, the median, and the mode are each seven for these data. In a perfectly symmetrical distribution, the mean and the median are the same. This example has one mode (unimodal), and the mode is the same as the mean and median. In a symmetrical distribution that has two modes (bimodal), the two modes would be different from the mean and median.

Source Image: medium.com
Download Image
Water | Free Full-Text | Application of an Interval Two-Stage Robust (ITSR) Optimization Model for Optimization of Water Resource Distribution in the Yinma River Basin, Jilin Province, China
Communication Design — Project 4 — Kyle Lee | by Kyle Lee | Medium Graph 2.2.1: Histogram for Monthly Rent. Notice the graph has the axes labeled, the tick marks are labeled on each axis, and there is a title. It is important that your graphs (all graphs) are clearly labeled. Reviewing the graph you can see that most of the students pay around $750 per month for rent, with about $1500 being the other common value.
Chapter 2 Flashcards | Quizlet Solved Look at the two histograms below. Each involves the | Chegg.com By Jim Frost 23 Comments. Histograms are graphs that display the distribution of your continuous data. They are fantastic exploratory tools because they reveal properties about your sample data in ways that summary statistics cannot. For instance, while the mean and standard deviation can numerically summarize your data, histograms bring your